Magnet Frequently Asked Questions
Click on the question below to scroll to the answer or scroll down to view all the questions and answers.
Where are the poles on these magnets?
To what temperature can Ceramic magnets be subjected before they start losing their magnetic force?
What are diametrically magnetized cylinder magnets?
What are the Gauss ratings of our magnets?
What does grade N42 , N45 or N52 mean?
Can I cut or drill neodymium magnets?
How long will Neodymium magnets last?
What are the tolerances of our magnets?
Questions
Pull Force is the amount of force required to separate 2 of the same size magnets from each other.
Actual pull force of cylinder/disc magnets may vary depending on different applications due to the small contact surface, please test them before usage
Rule of thumb is that the magnet will hold approx. 1/3 the weight of the stated pull force. So...If pull force stated is 90 lbs...the magnet will hold approx. 30 lbs in weight hanging from it.
Also..If you are trying to stick the magnet to stainless steel...the better the quality of the stainless steel...the less the magnet will stick.
Where are the poles on these magnets?
Just remember this:
For rectangle/bar magnets... All our rectangular magnets are magnetized through the thickness.. The poles are always on the surfaces of the 1st two numbers of the measurements.
On round magnets... The poles are always axially magnetized through the thickness...This means the poles are on the flat surfaces unless stated that they are diametrically magnetized which means the poles will be on the curved sides.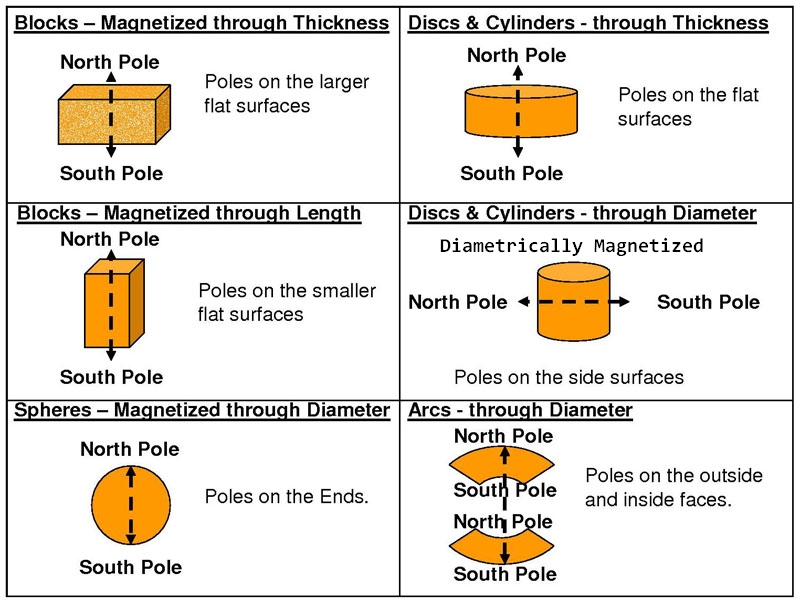
To what temperature can normal [non-SH] Neodymium magnets be subjected before they start losing their magnetic force?
176 degrees Fahrenheit or 80 degrees Centigrade.
To what temperature can Samarium Cobalt SmCo magnets be subjected before they start losing their magnetic force?
572 degrees Fahrenheit or 300 degrees Centigrade.
480 degrees Fahrenheit or 250 degrees Centigrade, but, the magnets should not be exposed to heating or cooling rate changes greater than 200°F or 93.3°C per hour.
Diametrically magnetized cylinder magnets have the poles (attraction) on the curved sides instead of on the flat ends.
The amount of magnetism [brmax at the center] of a magnet is measured in Gauss. This is a measure of the penetration of a magnet. Below is a table of the Gauss ratings of the most popular neodymium magnets:
Grade Gauss
N35 11,700-12,100
N38 12,100-12,500
N40 12,600-12,900
N42 12,900-13,200
N45 13,500-13,800
N48 14,000-14,200
N50 14,300-14,500
N52 14,600-14,800
The strength of neodymium magnets is given by a grading from N24 for the lowest strength magnets to N52 for the strongest we carry.
Each number higher is about 1% stronger than the previous number grade.
NO...With cutting or drilling there is both a fire or fracture hazard and the dust is toxic.
400 years...if not subjected to sharp impacts or higher than rated temperatures.
How do I separate strong magnets that have separators between them or get 2 strong magnets apart that have become stuck together?
For even bigger and stronger magnets we suggest 2 people. One to hold securely the magnet on the table and the other to hold securely and push the other magnet that is over the leading edge of the table down and away and then keep it away from the other magnet(s)
Less than 2": +/-0.002 inch
2" and above: +/- 0.004 inch
For Cup magnets, +/- 0.01"
The standard tolerance for ceramic magnets is +/- 2% of the dimensions except thickness. The tolerance for thickness is +/- 0.15mm.
